school: Other
News . Events Mobile Tools for Combating Slave Labor – SDG 8
Context
The Center for Combating Slave Labor and Human Trafficking (CETE) is based at UNEB Campus XVI in Irecê under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Ana Karine Loula Torres Rocha and her team including Prof. Ms. José Allankardec Fernandes Rodrigues and Prof. Dr. José Humberto da Silva (consultor). A key collaborator is UNEB’s Salvador campus, represented by Prof. Dr. Silvar Ferreira Ribeiro, Prof. Dr. Sônia Maria da Conceição Pinto, and Prof. Dr. Hebert Vieira Durães who coordinate open schooling initiatives. This initiative also receives support from UNEB’s Rector, Prof. Dr. Adriana dos Santos Marmori Lima, and benefits from international collaboration with the Open University UK, represented by Dr. Alexandra Okada.
In alignment with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), CETE utilizes open education and open schooling including mobile technologies to promote economic growth, inclusive and sustainable employment, and decent work for all, as well as SDG 4 (Quality Education). The Brazilian Constitution of 1988 affirms work as a social right, ensuring dignity and social protection for workers. However, many still face exploitative working conditions; slave labour remains a criminal offense under Article 149 of the Brazilian Penal Code.
Education and Social Inclusion as a Strategy for Preventing Slave Labor
In this context, CETE was created, the first clinic in the Northeast with this focus, as a proposal to confront this reality; within it, we commit to our political, scientific, and social vocation based on the relationship between UNIVERSITY – TERRITORY – DEVELOPMENT from the perspective of sustainability, science, technology, and innovation with social responsibility and open schooling. Supported by the CARE-KNOW-DO framework, one of the initial challenges of this project is to engage adult learners in reflecting on the local context, contributing to raising awareness of the condition of slave labor.
As a strategy to confront this issue, it is necessary to strengthen the interdisciplinary support network, integrating areas such as education, law, and health, in pursuit of actions promoting decent work and protecting human rights in the workforce, prioritizing vulnerable individuals and communities, promoting equal opportunities, and proposing regional and local development strategies that foster community bonds and inclusive, sustainable economic growth.
Among the activities already developed by the University of the State of Bahia in teaching, research, and outreach is its strong connection with public basic education schools, directly interacting with administrators, teachers, students, and their families. Youth and Adult Education (EJA), one of these fields, targets individuals who missed regular schooling, comprising a group of men and women, workers who, as verified, fit the profile of those recruited for seasonal farm work. Focusing on these individuals can be a relevant strategy to prepare them to face this harsh reality. Educating, raising awareness, preventing, and training for more skilled jobs can certainly help reduce their vulnerability, preventing recruitment into this illegal activity.
The Connect 2030 Project, already underway in the region in the cities of Ibipeba, Lapão, Irecê, and Presidente Dutra, supports this process by delivering science education based on real socio-scientific issues, involving families, other societal segments, university scientists, and policymakers, contributing over the past three years to improve local education and projects for expansion and consolidation of its results.
Today, CETE is part of a network of legal clinics in Brazil addressing slave labor and human trafficking, including:
- Slave Labor and Human Trafficking Clinic at the UFMG Law School / MG;
- CETE: Anti-Slave Labor Clinic at UNEB / BA;
- Human Trafficking and Slave Labor Clinic at João Pessoa University Center – UNIPÊ / PE;
- CETE – Anti-Slave Labor Clinic – UFU Law School / Uberlândia / MG;
- Slave Labor Combat Clinic (CCTE) – UFPA / PA;
- Exploitative Labor Combat Clinic (CCST) – UFBA / BA;
- Slave Labor Clinic UNIFACIG / MG;
- Slave Labor Combat Clinic UNIPAC – Uberaba / MG;
- Human Rights Clinic at UFMT / MT.
CARE:
This open education community supported by open schooling highlights the following project goals:
- Support and strengthen actions promoting Decent Work, developed by the public sector, social organizations, and private sector in the Irecê region;
- Implement strategies promoting decent work with the protection of human rights in the workforce, prioritizing vulnerable individuals and communities, promoting equal opportunities, and proposing a regional and local development strategy capable of strengthening community bonds and fostering inclusive, sustainable economic growth;
- Develop actions through social dialogue for mutual collaboration, respect, institutional capacities, and concrete actions, acting individually and collectively to promote decent work in the region, aiming at building a Network for Promoting Decent Work;
- Undertake preventive, intervention, and follow-up actions for individuals who are victims of slave labor and human trafficking across various fields such as education, law, and health.
KNOW:
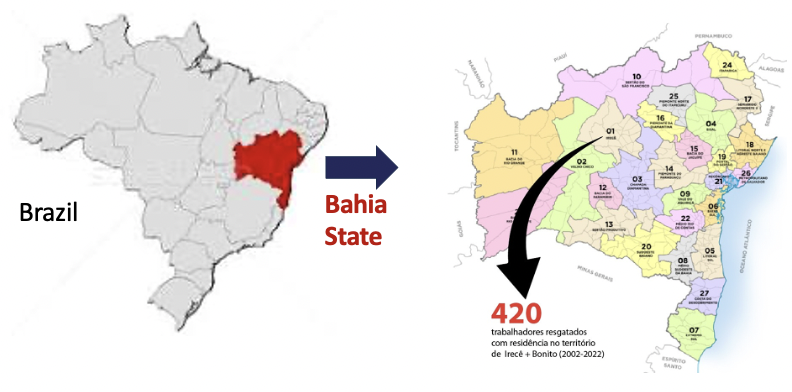
According to recent research, SmartLab 2023, in Brazil, among victims of slave labor, 64% are Black, with many having low levels of schooling, and most rescued victims are male (93%). In Bahia, Black individuals represent 80% of those rescued, with more than half not completing the 5th grade, and among them, 22% are illiterate. The majority are male (92%) and between 18-29 years old. Research by the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG) identified that Irecê / Bahia / Brazil has the highest percentage of modern enslaved individuals on coffee farms in Minas Gerais. Victims of contemporary slave labor and human trafficking are in a situation of grave social and emotional vulnerability.
Through research conducted by the Federal University of Minas Gerais – UFMG, between 2002 and 2022, it was identified that the region of Irecê / Bahia / Brazil had the highest percentage of modern enslaved individuals on coffee plantations in the State of Minas Gerais: 420 individuals. Victims of human trafficking for purposes of labor analogous to slavery, by the end of July 2024, in the interior of MG, on coffee farms, totaled 46, with these numbers: São Gabriel (06) / Lapão (03) / Mirangaba (01) / Canarana (13) / Irecê (01) / Morro do Chapéu (03) / Jussara (14) / Ourolândia (02) / Cafarnaum (03); at the end of August 2024, in the Federal District, at Grupo Pluma farms, an additional 10 individuals were counted: Xique-Xique (06) / Nova Ibiá (02) / Bonito (02). All these people, victims of contemporary slavery and human trafficking, are in a situation of severe social and emotional vulnerability.
DO:
Working Groups:
- Guidance / Legal support;
- Psychosocial health;
- Scientific Studies and Communication;
- Responsible Research and Innovation;
- Open Education with Open Schooling supported by STEAM and e-artvism;
- Professional Training / Capacity Building.
Actions:
- Participation and Contribution to the I Regional Seminar in Irecê on Decent Work;
- Signing of a Commitment Agreement between UNEB and UFMG, in addition to the Regional Pact for Promoting Decent Work;
- CETE Itinerant;
- Creation of a Research Group registered with CNPq;
- Offering an elective course in undergraduate and graduate studies;
- Participatory Design of Resources, Technologies, and Pedagogies for Open Schooling to raise awareness, prevent, and empower through partnerships between schools, universities, and professional experts.
Partnerships:
- OAB; Junior Company – CONSOL; FAEB / SENAR;
- Secretariat of Labor, Employment, Income and Sport – SETRE;
- Decent Work Institute – ICT; Coffee Program;
- Global Fund to End Modern Slavery – GFEMS;
- Network of Legal Clinics in Brazil;
- Open University / UK.

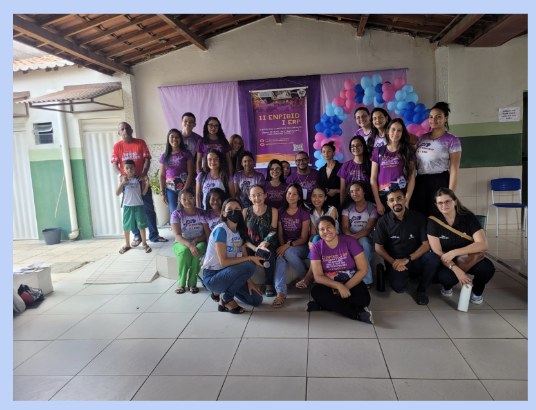
Photo: CETE – at UNEB Campus XVI in Irecê

Photo: CETE – at UNEB Campus XVI in Salvador
The integration of e-artivism into the CETE initiative at UNEB demonstrates how art and activism can amplify awareness of human trafficking and slave labor, fostering community engagement and driving systemic change through open schooling. By creatively combining digital tools, storytelling, and visual media, e-artivism enables students, educators, and communities to confront the harsh realities of exploitative labor and human trafficking.
Through the CARE-KNOW-DO framework, e-artivism encourages emotional engagement (CARE) by using impactful narratives and visual campaigns that evoke empathy and understanding of victims’ realities. In the KNOW phase, participants engage in research and discussions, analyzing socio-scientific data on slavery and trafficking to deepen their knowledge and identify root causes. Finally, in the DO phase, e-artivism mobilizes communities to take action, such as creating educational resources, organizing awareness campaigns, and collaborating with local and national stakeholders to promote Decent Work (SDG 8).
This approach not only educates but also empowers individuals and communities to actively participate in combating exploitative practices. By embedding e-artivism into open schooling, CETE leverages the transformative potential of art and activism to create a culture of awareness, prevention, and advocacy, aligning with the principles of inclusive and sustainable development.
REFERENCES:
CETE website :
https://www.ceteunebirece.org/
Nossa voz:
https://nossavoz.org.br
Literature:
Freire, P. (1996). Pedagogy of the oppressed (revised). New York: Continuum, 356, 357-358.
Freire, P. (1998). Pedagogy of freedom: Ethics, democracy, and civic courage. Rowman & Littlefield.
Research in the news:
Starbucks: slave and child labour found at certified coffee farms in Minas Gerais
News . Events Audio Visual artefacts for communities (SDG 11)
Fonte:Imagem recorte do vídeo Trilhas da Pedagogia – Disponível: IFECast https://youtu.be/RUkKhuhl–0?si=bfo0PIcXU_QVDIzq
Context:
This practice was part of the training of undergraduates in the Pedagogy Course at the Federal University of Cariri (UFCA), which was recently recognized with the highest score by the Ministry of Education (MEC). The course stands out for its interdisciplinary work, through which educators promote teaching, research, outreach, and culture.
This partnership with the Porteiras School began in 2022, due to research developed in the open schooling axis with digital technologies, in the Pedagogy course and a national partnership linked to CNPQ in which UFCA is connected to studies at UFRJ, UFF, PUC-SP, PUC-PR, UNEB, UFSC, and internationally with the Open University, with studies by Alexandra Okada.
One of the first challenges for Pedagogy undergraduates and basic education students was to open their windows. This process encouraged students to reflect on their local context, to investigate the socio-scientific topics that most interested them. Several disciplines were integrated, from the fields of art, technology, and curriculum, as seen in one of the videos from the exhibition of photo-narratives created by Francione Charapa, at IFE/UFCA.

After this journey of opening the windows for pedagogy students, we implemented an action-research project coordinated by Prof. Dr. Karine Pinheiro at Cirene Maria Esmeraldo School, involving research scholars such as Daniel Alberto, Emerson Gomes, Valeria Vieira, Vivila de Carvalho, Elizete da Silva, Luana Argentina, Marielly, and 85 pedagogy students. At Cirene Maria Esmeraldo School (Kessyo Santos, Thais Coelho, Maria do Socorro Silva and the basic education students at Cirene Maria Esmeraldo School in Porteiras), and in the cultural community at the Quilombo do Souza, with Master Maria de Tiê, Cyda Olímpio, Valéria Pinheiro CIAVATA, and Instituto Anjos Digitais. The project continues with the coordination of university extension activities, with the Freirean Movement led by Prof. Darliane Amaral and the appreciation of multiple cultural expressions, which was also supported by the Voices of Cariri Project, led by Prof. Dr. Ligia Rodrigues.
This open schooling community highlights two examples that integrate the use of digital technologies to support the training of educators focused on creative processes through various digital genres, fostering open schooling:

The first example was featured in the Teaching Initiation Program, particularly during the First Meeting of the Institutional Program of Teaching Initiation Scholarships (EnPibid/UFCA) and the First Meeting of the Pedagogical Residency Program (ERP/UFCA) at the Federal University of Cariri (UFCA). Approximately 20 papers were published by undergraduate students, who developed communication skills, teamwork, expanded vocabulary, and a decolonial perspective on the curriculum. As part of the intersectoral integration between the university and schools, 24 workshops and a thematic panel were developed in collaboration with the State University of Bahia (UNEB), alongside Professor Silvar Ribeiro. This connection reinforced the bond between the university, schools, and the community.
The second example refers to activities in a basic education school in the municipality of Porteiras, aimed at analyzing the educational projects developed by basic education students. These projects were aligned with the pillars of open schooling and the development of the C5 Generation (creative, critical, collaborative, communicative, and civic-minded). In both examples, literacy and scientific education were promoted from basic education onward, embedded within a cybercultural context, involving undergraduates, teachers, and students engaged in open schooling.
CARE:

The undergraduate students in the Pedagogy Program at the Institute of Educator Training were involved in research, outreach, and cultural projects tied to real-life themes from their community. These activities occurred both at the university, with courses like Digital Technologies and Pedagogical Innovations, and in basic education schools. Guided by Professor Karine Pinheiro, these initiatives expanded research in basic education and established partnerships between schools, the community, and the third sector, focusing on the creation of school projects using the open schooling approach.
KNOW:

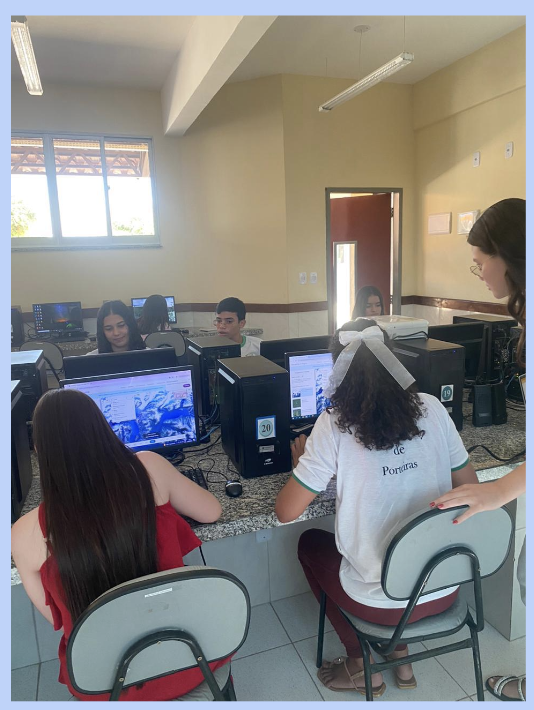
The project engaged digital natives (Prensky, 2010), who developed creative processes through new digital genres, experiencing the power of technology to express ideas in multiple forms. We observed a growing use of video, with students sharing stories, reels, and TikTok videos. Consequently, the cultural practice of using images was intensified with audiovisual production, marked by the multimodal nature of language in the cybercultural context (Santos, 2014). Through various disciplines, students experienced this new approach, incorporating fieldwork where they encountered popular, scientific, and cultural knowledge, all of which had unimaginable impacts on open schooling (Okada, 2016).
In addition, several workshops were designed to map concrete issues and geographic areas using Google Earth to identify locations, aiming for authentic co-learning.
DO:

The educational projects developed by students during 2023-2024 involved multiple societal actors, reinforcing democratic practices, valuing diversity, promoting solidarity, and addressing environmental issues. These initiatives fostered autonomy, helping students become active citizens within their community. This process was grounded in the principles of open schooling for the development of scientific education, open access, public engagement, and governance.
Through these activities, students became cultural producers on themes such as solid waste, cultural heritage, water conservation, and animal protection. Another highlighted competence was the expansion of socio-scientific vision. Both basic education and university students presented their projects at scientific events. As a result of this study, we introduce a Podcast Channel with around 1,800 views, showcasing the active involvement of cultural practitioners, who became reflective producers and developed a situated practice through continuous debate. The impact of this activity at the UFCA Brejo Santo campus became “glocal” (Silva, 2005).

Image – Recycling Workshop and Selective Waste Collection Campaign
Source: Produced by the authors
Results from Teachers (Six basic education teachers from Cirene Maria Esmeraldo Municipal School):
Pedagogical innovation using real, relevant contexts for students related to:
- SDG 15 – Animal protection, solid waste management
- SDG 4 – Cultural heritage
- SDG 16 – Water conservation
Publication of 14 scientific papers: ENPIBID/2023, IV Biology Meeting (IFE/UFCA).
Results from Undergraduate Students – Pedagogy (85 students) and Basic Education Students (Municipality of Porteiras):
Creation of an educational device – IFECast: My Community, a project involving interdisciplinary undergraduates and pedagogy students. The project involved various pedagogical moments for engagement within the IFE/UFCA community, through open schooling, exploring identity, meaning, and practice. This was facilitated by problematizing their reality.
We share the channel for this C5 Generation of Co-Entrepreneurs – IFECast: My Community, featuring audiovisual narratives about field visits to quilombola communities, environmental trail discoveries, storytelling creation, photo-narrative exhibitions, and interviews that inspired teaching discoveries through diverse digital genres. About 45 videos are available at: YouTube Channel: IFECast: My Community and on Instagram at: @ifecast_ufca.

News . Events Digital Inclusion for Equality (SDG 10)
This project was carried out with traditional communities, focusing on digital literacy, sustainable development and solidarity economy. These activities were integrated into local practices of handicrafts and family farming, two key economic pillars for these communities. Additionally, the project emphasized gender equity, giving a voice and space to women, the majority of whom are homemakers, students, and teachers. The participants’ ages and occupations were diverse, including young adolescents in basic education, teachers, and artisan workers. There was also significant ethnic diversity, representing different traditional ethnic groups from Ceará. The project incorporated Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 4 (Quality Education), 5 (Gender Equality), 10 (Reduced Inequalities), and 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), aiming to bring real and sustainable change to the lives of these communities.
Theme: Digital literacy, sustainable development and solidarity economy were the central themes of the activities. Digital literacy was seen as an essential tool for the participants, allowing them not only to learn how to use technology but also to apply it in their daily realities, especially in strengthening their economic initiatives. The sustainable development and solidarity economy was explored as a collaborative model, where artisanal production and family farming are viewed not just as sources of income but also as forms of resistance and autonomy for these communities.

CARE: One of the standout groups was “Trama de Mulheres Pretas” (Weave of Black Women), which has a long tradition in producing handicrafts and local foods. These women faced several challenges in using digital technologies, especially in seeking information, communicating, and promoting their products. The lack of access to technology and initial unfamiliarity with its potential hindered their economic growth and the visibility of their work. However, with the project’s support, they gradually overcame these barriers, acquiring new digital skills that allowed them to expand their networks and reach new markets.
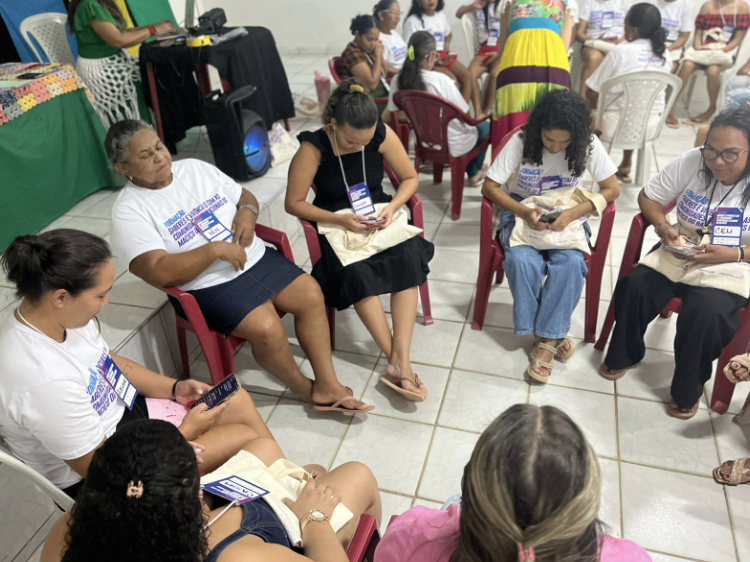

KNOW: Knowledge sharing was one of the pillars of the project, particularly in terms of forming associations and strengthening local entrepreneurship. Through workshops and continuous training, participants developed skills in management, organization, and marketing of their products, increasing their ability to act independently. Furthermore, understanding the dynamics of the solidarity economy was crucial for the women to realize the power of cooperation and self-sufficiency in their communities. They began to see their traditional practices in a new light, integrating them into a broader context of collaborative economy.
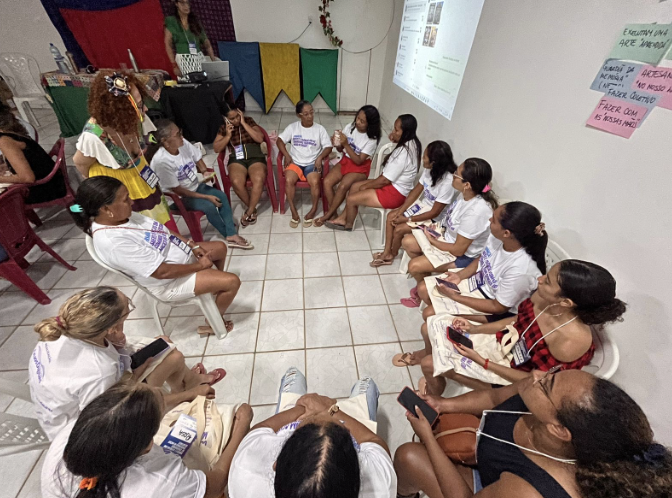

DO: One of the project’s most significant outcomes was the production of videos by the participants themselves, in which they shared their stories, challenges, and achievements. These videos were published on YouTube, serving as a platform for their voices to be heard beyond local boundaries. This initiative not only expanded the visibility of the women’s work but also boosted their self-esteem and recognition of their capabilities. The creation of these videos was an empowering process, where each woman could share her journey of overcoming obstacles and personal growth, inspiring other women and communities.

Impact on Education: The project had a profound impact on how the participating women and their communities viewed education. By addressing local problems collaboratively, the project facilitated co-learning between the women and the facilitators, aligning the training with the challenges faced by the communities. This process resulted in a deeper understanding of the challenges encountered by the women in both personal and professional spheres. The unity and solidarity that emerged from this shared learning strengthened bonds among the participants and generated collective solutions to the problems they face daily.
Impact on Participants: Through observation and active engagement in the project, the women rediscovered the “right to dream” and began to believe in the possibility of improving their lives. Many reported that before the project, they felt limited by circumstances and the few opportunities available. As the activities developed, they started to envision new horizons. One of the participants summed up this transformation by saying, “Today I give myself the right to dream, and I can improve my life.” Another added, “Now I can dream.” The contact with other women involved in the project brought strength and motivation to the trainers, educators, and managers from the NGO Anjos Digitais, as one of them shared: “Being in contact with these women gives me strength. Even though it seems small, it’s enormous for them.” The experience also highlighted the importance of affection and mutual support, creating a space where everyone could learn and grow as equals. “We arrived as equals and co-learned together, on equal footing,” said another participant, reflecting on the spirit of cooperation that permeated the entire process. This feeling of unity and solidarity, through the “CARE-KNOW-DO together,” filled the hearts of the participants with love and energy, empowering them to face new challenges and paving the way for future actions.
The project “Knowledge and Experiences with Traditional Communities of the Maciço do Baturité” exemplifies e-artivism by blending digital literacy, cultural preservation, and storytelling to empower communities and amplify their voices. Through the integration of traditional crafts and family farming with digital tools, participants transformed their practices into acts of advocacy, highlighting the importance of local culture and economic autonomy.
By producing videos to share their stories and challenges, participants used digital platforms as tools for creative expression and activism, expanding their reach and fostering awareness beyond local boundaries. This digital storytelling not only promoted their work but also inspired broader audiences, turning their personal narratives into a collective call for social and economic justice.

E-artivism in this project bridged traditional knowledge with modern technology, fostering co-learning and collaboration. Participants gained skills that allowed them to actively engage with and address pressing issues in their communities while creating opportunities for sustainable development. This initiative demonstrates the transformative potential of e-artivism to combine art, technology, and activism in creating pathways for empowerment and lasting change.

For more details: https://anjosdigitais.org/
News . Events CONNECT BOOK 2023
News . Events STOP – FOOD WASTE!
Care: The students were interested in a real-life issue related to responsible food consumption that represents a conscious food choice, taking into account aspects related to our decisions regarding health, environment, economy, culture, etc. Carrying out social responsibility activities plays an important role in how participants will understand why making any decision about personal food can have negative consequences / irreversible on an important part of our planet. . The students who participated in the activities were students aged 3-18, from preschool, primary, secondary and high school. A total of 825 students participated in these activities.
Know: Students used knowledge about food waste by watching documentaries on the effects of food waste, conducting a case study at economic agents in the city – 3 restaurants, by visiting the bread factory in the city, making leaflets with information through which we can reduce food waste, making a trophic pyramid, healthy breakfast and making figurines of fruits and vegetables, drawing up posters.
The competences that the students practiced were:
- Motivating students to adopt a balanced and economical lifestyle;
- Encouraging students to find practical and effective ways to reduce food waste;
- Developing interdisciplinary connections to draw public attention to food waste;
- Changing the attitude of students, their families, school teachers towards food waste.
Do: At the end, students prepared posters, leaflets, posters, interview, video. They carried out the activities in groups but also individually, being supported by family and community members.
Findings related to the Open Schooling approach: The activity was framed in the curriculum. It was challenging and useful because students’ confidence and self-esteem increased as a result of participating in complex activities that highlighted their abilities and required them to make decisions. The improvement of social skills was reflected through cooperation at the level of working groups and students’ roles in this context, through the relationship with colleagues in school. Open schooling could be challenging for other teachers because it increases creativity levels among both teachers and students.
Results obtained by students: Students were interested in the topic proposed for research and showed interest in participating in other activities aimed at the practical and applicative character of the given topic
News . Events In the CFGM of Pharmacy we promote our mental health
Care Stage: The students of the CFGM of Pharmacy made an analysis about health and its three branches and were very interested in working on the promotion of their mental health during their stay at the educational center. A total of 38 students participated in two groups (morning and afternoon).
Know stage: During the participatory research phase, during which they identified their needs and devised an action plan, students utilized their knowledge of mental health and habits. Additionally, they actively applied skills such as planning, organization, information retrieval, self-directed learning, and the application of acquired knowledge.
Do stage: Students conceived and implemented a mental health promotion action plan comprising four distinct activities. It was the students themselves who lead the sessions at the classroom.
Results related to the Open Schooling approach: Undoubtedly, participatory research has allowed them to not only develop the professional, personal, and social skills outlined in the curriculum of the CFGM Pharmacy and Parapharmacy but also provided them with the opportunity to enhance key cross-cutting skills essential for their future profession, such as autonomy, work organization, responsibility, and teamwork. Certainly, the inclusion of social actors in this research can further facilitate the cultivation and acquisition of these competencies and knowledge.
Support for the implementation of educational resources by: head of department
Student results: The students enthusiastically embraced the proposal and eagerly accepted the challenge to participate. We believe that this initiative has served as an excellent opportunity to shed light on the significance of mental health issues among young people. Simultaneously, it has enabled us to foster certain skills among the students through the application of scientific methodology throughout the entire process.
News . Events In the CFGM of Pharmacy we promote our mental health
Care Stage: The students of the CFGM of Pharmacy made an analysis about health and its three branches and were very interested in working on the promotion of their mental health during their stay at the educational center. A total of 38 students participated in two groups (morning and afternoon).
Know stage: During the participatory research phase, during which they identified their needs and devised an action plan, students utilized their knowledge of mental health and habits. Additionally, they actively applied skills such as planning, organization, information retrieval, self-directed learning, and the application of acquired knowledge.
Estapa Do: Students conceived and implemented a mental health promotion action plan comprising four distinct activities. It was the students themselves who lead the sessions at the classroom.
Results related to the Open Schooling approach: Undoubtedly, participatory research has allowed them to not only develop the professional, personal, and social skills outlined in the curriculum of the CFGM Pharmacy and Parapharmacy but also provided them with the opportunity to enhance key cross-cutting skills essential for their future profession, such as autonomy, work organization, responsibility, and teamwork. Certainly, the inclusion of social actors in this research can further facilitate the cultivation and acquisition of these competencies and knowledge.
Support for the implementation of educational resources by: head of department
Student results: The students enthusiastically embraced the proposal and eagerly accepted the challenge to participate. We believe that this initiative has served as an excellent opportunity to shed light on the significance of mental health issues among young people. Simultaneously, it has enabled us to foster certain skills among the students through the application of scientific methodology throughout the entire process.